Did you know that carbon dioxide (CO2) is more than just a greenhouse gas? It actually plays a vital role in the functioning of our bodies. From controlling our rate and depth of breathing to influencing the production of virulence factors in certain bacteria, CO2 is a key player in our health. Understanding how carbon dioxide interacts with proteins and influences biological systems could lead to groundbreaking advancements in therapeutics and disease management. By delving into the intricate ways CO2 affects our bodies, researchers are uncovering new possibilities for improving human health and well-being.
In addition to its impact on human health, CO2 also plays a crucial role in biotechnology and agriculture. Plants and photosynthetic organisms rely on carbon dioxide as a primary carbon source to grow and sustain their life cycles. By studying the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms and how CO2 binds to proteins, researchers are gaining valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms through which this gas affects biological systems. The Canadian Light Source (CLS) and synchrotron technology have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of CO2 and its various roles in both human health and agricultural practices.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
The Importance of CO2 in Health
How CO2 affects physiological functions
Carbon dioxide (CO2), often viewed negatively due to its impact on climate change, actually plays a critical role in human health. Within the body, CO2 serves a crucial function in regulating physiological processes. From controlling breathing rates to impacting immune responses, CO2 is essential for maintaining optimal health.
The role of CO2 in immunity
CO2 influences immunity by affecting the expression of virulence factors in bacteria. Certain bacteria, like Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax, increase the production of these virulence factors in the presence of high CO2 concentrations. Understanding how CO2 influences these pathways could potentially lead to therapeutically targeting them to combat bacterial infections effectively.
CO2 in controlling breathing rate
In humans, CO2 is essential in regulating the rate and depth of breathing. The central brain stem uses CO2 levels as a signal to adjust breathing patterns. Proper CO2 levels are crucial for maintaining respiratory function and overall well-being.
CO2 and Disease Pathways
CO2’s impact on virulence factors in bacteria
CO2 plays a significant role in modulating the expression of virulence factors in pathogenic bacteria, affecting their ability to grow and evade the immune system. By better understanding these pathways influenced by CO2, potential therapeutic interventions could be developed to combat bacterial infections effectively.
CO2’s suppression of inflammatory responses
CO2 has been shown to suppress inflammatory responses in the body. This has implications for various inflammatory disorders that are challenging to control. By studying how CO2 influences these pathways, researchers may uncover new ways to manage and treat inflammatory conditions more effectively.
Therapeutic implications of understanding CO2 pathways
Understanding the intricate ways in which CO2 influences disease pathways and immune responses can have significant therapeutic implications. By targeting these CO2-mediated pathways, novel therapeutic approaches could be developed to treat a variety of health conditions, ranging from bacterial infections to inflammatory disorders.
CO2 in Biotechnology and Agriculture
Plants as carbon dioxide consumers
Plants and other photosynthetic organisms utilize CO2 from the atmosphere as their primary carbon source for photosynthesis. CO2 is a vital component in the process of converting light energy into chemical energy, allowing plants to grow and sustain their life cycles.
The role of CO2 in photosynthesis
CO2 is a critical molecule in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert CO2 into carbohydrates and sugars essential for their growth. Understanding how CO2 interacts with plants at the molecular level is crucial for improving agricultural practices and enhancing crop production.
Applications in biotechnology research
CO2’s association with plant growth and photosynthesis makes it a valuable resource in biotechnology research. By studying the effects of CO2 on plants and photosynthetic organisms, researchers can develop innovative solutions for agricultural challenges and contribute to sustainable food production.
Striking the Right Balance: Maintaining Optimal CO2 Levels
Effects of high CO2 levels in the environment
While CO2 is essential for various physiological functions, high levels of CO2 in the environment can have detrimental effects on global climate patterns. Excessive CO2 emissions contribute to climate change, leading to rising temperatures and environmental degradation.
The dangers of CO2 deficiency in the body
CO2 deficiency in the body can result in lightheadedness, dizziness, muscle cramps, fatigue, confusion, and even seizures in severe cases. Maintaining optimal CO2 levels is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Symptoms of CO2 deficiency
Recognizing the symptoms of CO2 deficiency, such as tingling in the hands and feet, is essential for preventing adverse health effects. Monitoring CO2 levels in the body and ensuring adequate ventilation are key in preventing CO2 imbalances.
This image is property of sierrasleepwell.com.
Understanding CO2 Levels in the Body
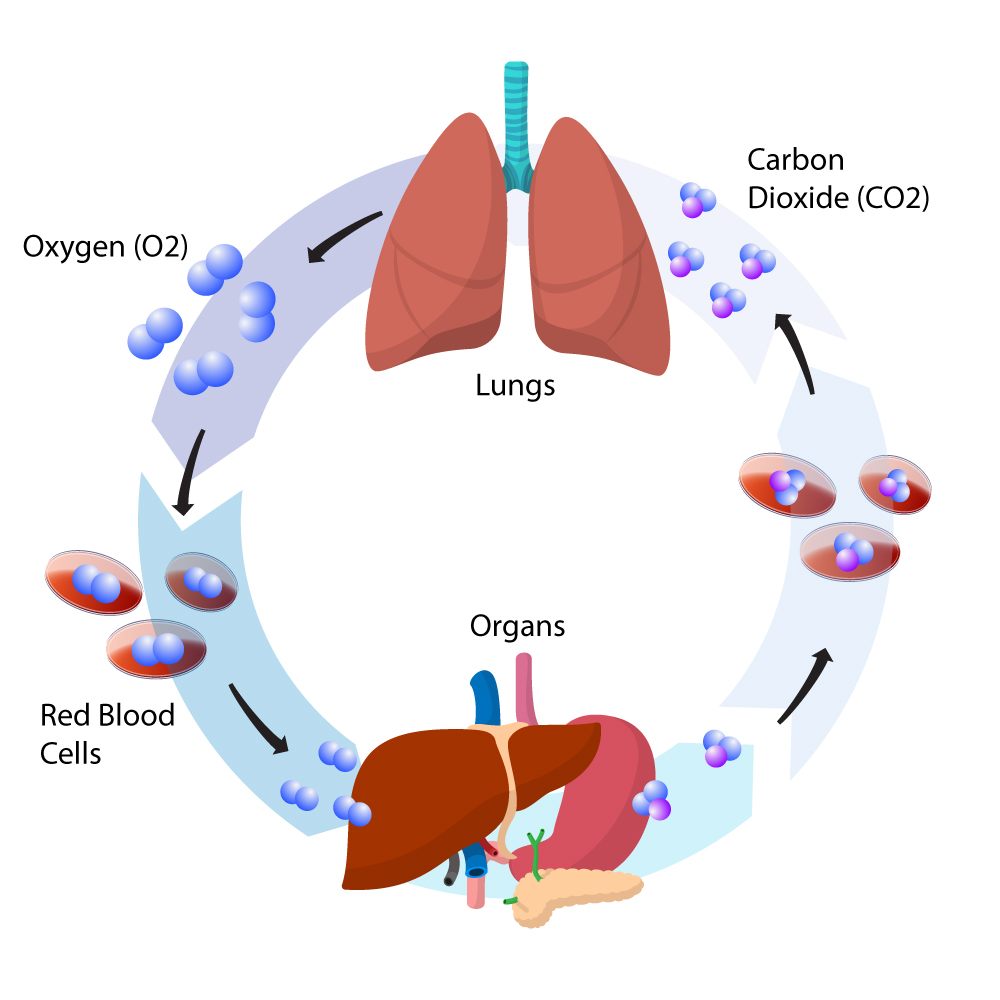
Regulation of CO2 levels in the bloodstream
The body tightly regulates CO2 levels in the bloodstream through mechanisms like the carbonic anhydrase enzyme. This enzyme plays a critical role in transporting CO2 and maintaining acid-base balance in the body.
Carbonic anhydrase enzyme and CO2 transport
The carbonic anhydrase enzyme facilitates the conversion of CO2 to bicarbonate ions, allowing for efficient transport of CO2 from tissues to the lungs for elimination. Disruptions in this process can lead to imbalances in CO2 levels and impact overall health.
Effects of CO2 imbalance on health
Imbalances in CO2 levels can have significant health implications, affecting respiratory function, acid-base balance, and overall metabolic processes in the body. Understanding the effects of CO2 imbalances is crucial for managing various health conditions and promoting well-being.
CO2 Monitoring in Healthcare
Diagnostic tools for measuring CO2 levels
Healthcare professionals utilize various diagnostic tools and tests to measure CO2 levels in the body accurately. Monitoring CO2 levels is essential for assessing respiratory function, acid-base balance, and overall metabolic health.
Treatment strategies for CO2-related disorders
Treating CO2-related disorders involves addressing the underlying cause of CO2 imbalances and restoring optimal CO2 levels. Therapeutic interventions may include respiratory support, medication, and lifestyle modifications to manage CO2 levels effectively.
Monitoring CO2 in critical care settings
In critical care settings, continuous monitoring of CO2 levels is vital for assessing patients’ respiratory status and guiding treatment interventions. Healthcare providers use advanced monitoring technologies to ensure accurate and real-time assessment of CO2 levels in patients.
This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
Environmental Impact of CO2
CO2 emissions and climate change
Excessive CO2 emissions from human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, contribute to climate change. Rising CO2 levels in the atmosphere lead to global warming, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events with far-reaching environmental consequences.
Global efforts to reduce CO2 levels
International efforts are underway to reduce CO2 emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Initiatives like the Paris Agreement aim to limit global temperature rise by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including CO2, to transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Carbon sequestration technologies
Carbon sequestration technologies offer innovative solutions for capturing and storing CO2 emissions from various sources, like power plants and industrial processes. These technologies help reduce CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere and combat climate change effectively.
CO2 as a Double-Edged Sword
The dual nature of CO2 in health and the environment
CO2’s dual role as a vital molecule in human health and a greenhouse gas contributing to climate change highlights its complex nature. Balancing the benefits of CO2 in physiological functions with its detrimental effects on the environment requires careful consideration and strategic interventions.
Balancing benefits and risks of CO2 exposure
Understanding the benefits and risks of CO2 exposure is essential for making informed decisions about CO2 management. While CO2 is essential for various biological processes, mitigating its environmental impact is crucial for preserving ecosystems and combating climate change.
Ethical considerations in CO2 management
Ethical considerations surrounding CO2 management involve balancing the needs of human health with environmental preservation. Prioritizing sustainable practices and reducing CO2 emissions can help minimize the adverse effects of CO2 exposure on both human health and the environment.
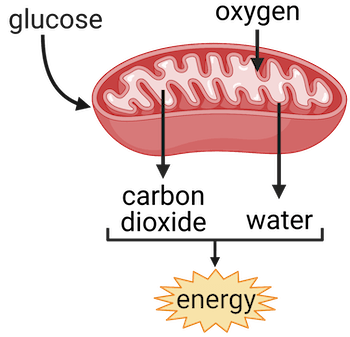
This image is property of cdn.kastatic.org.
Future Research and Innovations in CO2 Studies
Emerging technologies for CO2 research
Advancements in technology continue to enhance research on CO2 and its implications for human health and the environment. Innovations in monitoring tools, biochemical analysis, and computational modeling offer new avenues for studying CO2 pathways and developing targeted interventions.
Potential applications of CO2 findings in medicine
The insights gained from CO2 research have the potential to inform novel therapeutic approaches in medicine. Understanding how CO2 influences disease pathways could lead to the development of innovative treatments for various health conditions, offering new options for patient care.
Implications for public health policies
The findings from CO2 research have broader implications for public health policies and environmental regulations. Integrating scientific evidence on CO2’s role in health and climate into policy decisions can promote sustainable practices, enhance healthcare outcomes, and support global efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
Summarizing the multifaceted role of CO2 in human health and the environment
Carbon dioxide (CO2) plays a multifaceted role in human health, influencing physiological functions, immunity, and disease pathways. While essential for various biological processes, CO2 also poses environmental challenges, contributing to climate change and global warming. Striking the right balance between harnessing the benefits of CO2 in health and mitigating its environmental impact is crucial for sustainable living.
Highlighting the need for further research and informed decision-making
Further research into CO2’s intricate mechanisms and its implications for human health and the environment is necessary to advance scientific knowledge and develop effective interventions. Informed decision-making based on scientific evidence will be key in addressing the complex challenges posed by CO2 and promoting global sustainability and well-being.
